Classification Of Alcohols.
Compounds inward which a hydroxyl grouping is attached to an aliphatic carbon atom are called alcohols. Alcohols are classified equally monohydric, dihydric in addition to trihydric, depending upon the discover of hydroxyl groups they comprise inward their molecules. Alcohols containing ane hydroxyl grouping inward their molecules are called monohydric alcohols in addition to the alcohols containing ii in addition to iii hydroxyl groups on unlike carbon atoms inward their molecules are called dihydric in addition to trihydric alcohols, respectively. The alcohols having to a greater extent than than ane hydroxyl grouping inward their molecules are to a greater extent than oft than non called polyhydric alcohols.
Method Of Preparation Of Alcohols.
1. Hydrolysis of Alkyl Halides.
2. Hydration of Alkenes.
The acid-catalyzed add-on of H2O to an alkene gives alcohol. The acids most commonly to catalyze the hydration of alkenes are sulphuric acid in addition to phosphoric acid. The add-on of H2O to the double bond follows Markovnikov's rule. Alkenes react alongside sulphuric acid to attain alkyl hydrogen sulfates which on dilution alongside H2O followed past times heating are hydrolyzed to alcohols.
Acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes does non yield primary alcohols except ethanol. It yields alone secondary in addition to third alcohols. This method is to a greater extent than oft than non used for the production of alcohols on the industrial scale.
3. Hydration through Hydroboration.
Diborane, B2H6, adds to an alkene double bond alongside the boron atom becoming attached to the less substituted carbon to cast trialkyl boranes, which on oxidation alongside H2O2, inward the aqueous base of operations give alcohols. Diborane adds equally borane, BH3. Hydroboration reactions are normally carried out inward diethyl ether or inward tetrahydrofuran (THF). The final result is an add-on of -H in addition to -OH alongside the -OH existence attached to the to the lowest degree substituted carbon (anti-Markovnikov add-on of H2O to double bond).
4. By Oxymercuration - Demercuration. The add-on of H2O to an alkene tin live on achieved indirectly through oxymercuration - demercuration. Alkenes react alongside mercuric acetate inward a water-tetrahydrofuran solution to cast hydroxyalkylmercury compounds which on reduction alongside NaBH4 yield alcohols. The internet final result of the ii steps is Markovnikov add-on of -H in addition to -OH.
5. Alcohols from Grignard Reagent.
The Grignard reagent reacts alongside aldehydes or ketones to cast an add-on chemical compound which on hydrolysis alongside dilute acid gives the corresponding alcohol. Formaldehyde alongside Grignard reagent gives primary alcohol. Aldehydes other than formaldehyde cast secondary alcohols in addition to ketones yield third alcohols.
6. By the activeness of Grignard reagent on epoxides. Grignard reagents react alongside ethylene oxide (epoxide) to give an additional production which on hydrolysis yields primary alcohol.
7. By the reduction of aldehydes, ketones, acids, in addition to esters. Alcohols tin live on easily prepared past times the reduction of aldehydes in addition to ketones either past times hydrogenation inward the presence of a metallic catalyst such equally Ni, Pt or Pd or past times the usage of chemic reducing agents such equally LiAl H4 or NaBH4.
Catalytic hydrogenation has a drawback that it too reduces other functional groups such as
if acquaint inward the molecule.
LiAl H4 gives a really proficient yield of alcohols from aldehydes, ketones, acids, esters, acid chlorides in addition to acid anhydrides inward ethereal solution. One wages of this reagent is that it does non cut the olefinic bond in addition to hence tin reduce unsaturated aldehydes, ketones, etc. , to unsaturated alcohols.
Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) is insoluble inward ether but is stable inward aqueous solution (LiAlH4, is destroyed past times water). It is thence to a greater extent than oft than non used for the reduction of water-soluble aldehydes, in addition to ketones. NaBH4, is much less reactive in addition to therefore more selective in addition to reduces alone aldehydes in addition to ketones.
6. By the activeness of Grignard reagent on epoxides. Grignard reagents react alongside ethylene oxide (epoxide) to give an additional production which on hydrolysis yields primary alcohol.
7. By the reduction of aldehydes, ketones, acids, in addition to esters. Alcohols tin live on easily prepared past times the reduction of aldehydes in addition to ketones either past times hydrogenation inward the presence of a metallic catalyst such equally Ni, Pt or Pd or past times the usage of chemic reducing agents such equally LiAl H4 or NaBH4.
Catalytic hydrogenation has a drawback that it too reduces other functional groups such as
if acquaint inward the molecule.
LiAl H4 gives a really proficient yield of alcohols from aldehydes, ketones, acids, esters, acid chlorides in addition to acid anhydrides inward ethereal solution. One wages of this reagent is that it does non cut the olefinic bond in addition to hence tin reduce unsaturated aldehydes, ketones, etc. , to unsaturated alcohols.
Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) is insoluble inward ether but is stable inward aqueous solution (LiAlH4, is destroyed past times water). It is thence to a greater extent than oft than non used for the reduction of water-soluble aldehydes, in addition to ketones. NaBH4, is much less reactive in addition to therefore more selective in addition to reduces alone aldehydes in addition to ketones.
Industrial Preparation of Alcohols.
Manufacture of Methanol. At ane time, most methanol was produced past times the destructive distillation of woods in addition to therefore, was called "wood alcohol". Today most methanol is manufactured from marsh gas obtained from natural gas. Methane gas is passed alongside steam over Ni nether pressure level in addition to at a temperature of 900°C.
The mixture of CO in addition to H2 gases is passed over a heated copper catalyst nether pressure level to attain methanol.
Manufacture of Ethanol. Ethanol is the alcohol of wine, beer, whiskey, and similar beverages in addition to tin live on made past times the fermentation of sugars inward the presence of yeast.
The primary sources of sugars are molasses (waste from cane-sugar industries). The molasses is diluted alongside H2O so that the concentration of carbohydrate comes downward to about 10%. It is boiled in addition to acid is added till its pH becomes 4. This solution known as a wart, is mixed alongside yeast in addition to kept at 35°C inward large tanks. The following reactions are involved inward the fermentation of sugars.
If the source for carbohydrate is starch, in addition to so the starchy materials are converted into a squelch that is treated alongside malt, from germinating barley in addition to contains the enzyme diastase. This enzyme converts starch into maltose which is in addition to so subjected to fermentation alongside yeast to teach ethanol.
The unsmooth alcohol thus obtained is subjected to fractional distillation whereby 95% ethanol called 'rectified spirit' is obtained. To obtain 100% pure ethanol, called as absolute alcohol, it is mixed alongside benzene. Benzene forms an azeotrope with ethanol in addition to water. Azeotropic distillation of the mixture gives iii major fractions. The offset fraction contains a mixture of Benzene, ethanol, in addition to water, the minute fraction contains in addition to ends the terminal fraction is pure ethanol.
Physical Properties Of Alcohols.
Lower alcohols are colorless, toxic liquids in addition to are miscible alongside H2O inward all proportions. Their H2O solubility may live on attributed to intermolecular hydrogen bonding betwixt the molecules of alcohols in addition to water. But alongside the increment inward the number of carbon atoms, the solubility of alcohols inward H2O gradually. Among isomeric alcohols, the solubility increases alongside the increment inward branching. For example, tert - butyl alcohol is completely miscible alongside water. but the other three butyl alcohol is are alone moderately soluble inward water.
The Boiling indicate of alcohol shows a regular increment alongside the increment inward the discover of carbon atoms due to the increment inward van der Waals interactions. Among isomeric alcohols, equally branching increases the boiling points decrease. Boiling points of alcohol are much higher than those of the corresponding alkanes. The relatively high boiling points of alcohols tin live on attributed to the association of molecules through hydrogen bonding.
Chemical Reaction Of Alcohols.
Chemical reactions of alcohols ask either O-H or C-O bond cleavage. Some of the of import reactions of alcohols are described below.
1. Reaction alongside Active Metals (Alcohols equally Acids).
Alcohol reacts alongside active metals similar Na, K or Mg to cast alkoxides alongside the development of hydrogen gas.
The inward a higher house reactions present that alcohols are acidic inward nature. This is because that the O - H bond inward alcohols is polar in addition to allows the unloose of the hydrogen atom as proton (H+). However, alcohols are slightly weaker acids than water. This is because the alkyl groups inward alcohols bring an electron - releasing inductive effect. They unloose electrons towards the oxygen atom so that it becomes negatively charged. This negative accuse on oxygen makes the unloose of positive proton to a greater extent than difficult. The social club of acidity of alcohols is methyl > primary > secondary > third alcohol.
2. Reaction alongside Acid Halides in addition to Acid Anhydrides (Acetylation).
3.Reaction With carboxylic acids ( esterification).
Alcohol reacts alongside carboxylic acids on heating inward the presence of the catalytic sum of sulphuric acid to cast esters. The reaction is known equally esterification. The reaction is reversible in addition to tin live on shifted inward the frontward direction past times removing H2O equally before long equally it is formed.
Conc, H2SO4 acts equally a protonating agent equally good equally a dehydrating agent. Only primary alcohols genie proficient yields of esters. Steric hindrance is an of import constituent is esterification. Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 highly branched alkyl grouping is either the alcohol or the acid volition dull downward the charge per unit of measurement of esterification in addition to too shift the equilibrium to a greater extent than to the left side of the esterification reaction. The social club of reactivity of alcohol alongside given organic acid is, therefore, equally Primary Alcohol > Secondary Alcohol > Tertiary alcohol.



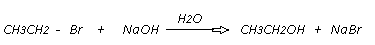






















No comments:
Post a Comment